Sound money and gold standard
Sound money is a kind of money that is not prone to sudden appreciation or depreciation in purchasing power over the long term. The stability of sound money is achieved through self-correcting mechanisms that are part of the free market system. We can say that supply and demand determine the purchasing power of sound money.
The concept of sound money evolved in the 19th century as many countries adopted the gold standard. It became associated with commodity money or hard currency. The country currencies or paper money has a value directly linked to gold. Countries agreed to convert paper money into a fixed amount of gold. A country that uses the gold standard sets a fixed price for gold and buys and sells gold at that price. It was always difficult to handle physical gold so that as early as the 19th century, gold served only as an underlying asset for paper and metal money.
For half a century beginning in 1879, Americans could trade in $20.67 for an ounce of gold. The country effectively abandoned the gold standard in 1933 as the Great Depression hit. Faced with mounting unemployment and spiraling deflation, the U.S. government found it could do little to stimulate the economy. To deter people from cashing in deposits and depleting the gold supply, the U.S. and other governments had to keep interest rates high, but that made it too expensive for people and businesses to borrow. So in 1933, President Franklin D. Roosevelt cut the dollar’s ties with gold, allowing the government to pump money into the economy and lower interest rates. The United States followed the gold standard until August 15, 1971, when President Richard Nixon announced that the government would no longer convert dollars to gold at a fixed value. Thus the gold standard was completely abandoned.
Note in particular the role of gold. Gold is naturally scarce. As long as the gold standard was followed, it was not possible to increase the amount of money in circulation. The gold standard is not currently used by any government in the world. The gold standard was completely replaced by fiat money. Fiat money describes a currency that is used because of a government’s order. Fiat money must be accepted as a means of payment. Today’s money is not sound any longer. The appeal of a gold standard is that it arrests control of the issuance of money out of the hands of imperfect human beings. With the physical quantity of gold acting as a limit to that issuance, a society can follow a simple rule to avoid the evils of inflation.
In today’s digital age, we aim to abandon banknotes and use only digital money. We can still use gold as the underlying asset for money. We can even avoid it and create pure digital scarcity. Let’s continue with cryptocurrencies and their chance to become sound money.
 Money backed by gold.
Money backed by gold.
Adoption triangle
Cryptocurrencies must succeed in at least these three categories in order to be able to become sound money: economy, technology, society. For the purpose of the article, let’s use a term adoption triangle for these three categories. Each category of the adoption triangle is important. Some categories may overlap in certain subareas. Individual projects will always differ in these categories and it will change over time. However, in order for sound money to be created and adopted, a project must be strong in all three categories. Let’s explain why.
Digital scarcity will not be here for a long time without a good incentive and economic model. The economic model can work only if the project will be adopted and the price of coins will rise. People will not adopt any technology if it does not work flawlessly, safely, and reliably. There cannot ever be a critical bug that would destroy the digital scarcity.
Technology must, by definition, solve a real problem or be useful. Great possibilities open up here. Cryptocurrencies can transfer value from one user to another. Is this property enough, or can cryptocurrencies do more? A blockchain is a trust machine. It can operate with smart contracts and build another layer of trust over sound money. Do we want it or not? Is a mere transaction system enough for sound money? If blockchain has the potential to disrupt not only finance but also social structures, isn’t it a better candidate for sound money? We don’t know any of that but we can discuss it.
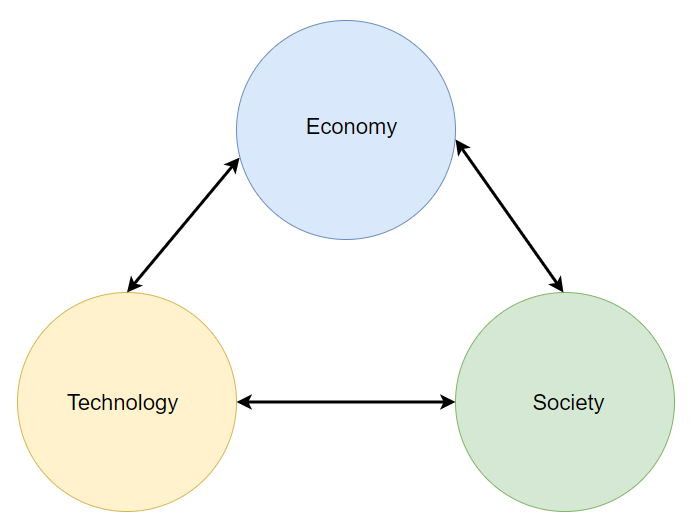 Adoption triangle
Adoption triangle
How to create a digital scarcity
From a technological point of view, it is relatively easy to create digital scarcity. The scarcity itself is just a number defined in the source code. The source code is available on GitHub and everybody can review it. The source code is used as an input to create a program or application. It happens during the so-called building process. The output of the build process is an executable application that can run on a given operating system. Let’s call it a full-node. You and other people can create own full-node or download already built version. The full-node behaves exactly as it is defined in the source code. In the case of cryptocurrency, the full-node usually tries to connect to peers, downloads blockchain, verifies all historical transactions up to the current block. When the full-node gets synced it starts to verify current blocks and you can send a new transaction. Full nodes of pool operators can propose new blocks.
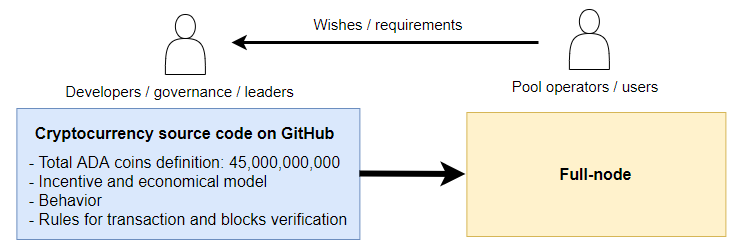 Full-node is created from the source code.
Full-node is created from the source code.
Regarding cryptocurrency, everything important is defined in the source code of the full node. There is a defined maximum number of coins, algorithms allowing the gradual release of coins under given conditions, algorithms needed to create a new transaction and block, algorithms for validating transactions and blocks, and many other things. A person who understands the source code of the project can verify all this. He or she can then create a full-node from the source code and join the distributed network as a new participant.
Digital scarcity is thus maintained through decentralization and secured by the security budget. In the case of the Cardano project, there will be circulating only 45,000,000,000 ADA coins. Notice that not only the number defining the maximum number of coins is important. The technology category would not work without the incentives and economic model of the project. At this point, it is necessary to ensure the long-term sustainability of the project and ensure the high-security level. It is in the best interest of the network that independent people keep it running for people. The network must therefore economically reward those who maintain it and punish those who cheat. Here, the technological category blends with the economic one. In order for the maximum number of coins in circulation to never change, the network must remain as decentralized as possible. It must be well secured at the same time. The security budget is different from project to project and there are significant differences between PoW and PoS network consensuses.
Some people believe that only the PoW consensus can serve as a solid base for sound money. Time will probably show that it is not necessary and we can easily achieve the same level of security via scientifically verified cryptography. PoW does a great job regarding security but gradually incline to centralization. So PoW definitely is not the best option for the network consensus and we have to continue with innovations.
People will only maintain the network if they are economically motivated to do so. At the same time, we must also think about people who have the right to modify the source code and who have decision power. Some comprehensible and democratic processes must be defined. It cannot be possible to adjust the protocol without social consensus. With this, we smoothly moved into the social category. There always be people behind the project. There will be developers, pool operators, maybe some leaders, or a strong team. We can see Blockstream and Square participating in Bitcoin development. There will always be groups of people who will want to determine the direction of further development. We can presume that the importance of public networks will rise. In time, we can expect some quarrels about which direction to go. Sooner or later, each project will come to the point where a complex and unpopular decision will have to be made. The source code will never be ready for all possibilities. External conditions change every day and each technology needs updates. As history has shown, without timely major updates to the source code, the properties of the protocol deteriorate. Project governance is considered as an inevitable part of a well-decentralized project.
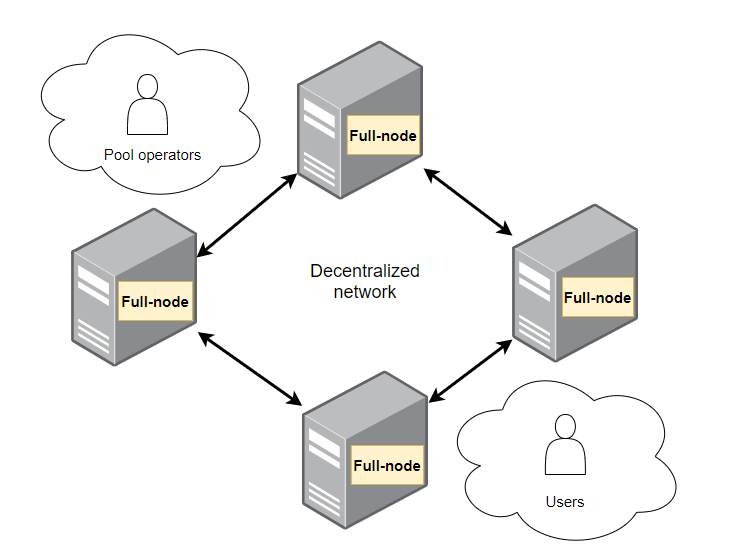 Full-nodes keep digital scarcity. Pool operators usually propose blocks and users can validate them.
Full-nodes keep digital scarcity. Pool operators usually propose blocks and users can validate them.
As you can see, we touched all three categories when we talked about the creation of digital scarcity. As it is easy to write an arbitrary number into source code, it might be very difficult to maintain it in the long term. Let’s conclude that we have a technology that allows us to create digital scarcity and we are in the testing phase. It is easy to program an inflation curve into the source code of a distributed protocol. However, it is difficult to predict the future. No one knows exactly what the inflation curve should look like. In fact, we do not even know whether it is better to cap the maximum number of coins or to use some inflation model. If we want to be prepared for the future, we may need some voting system that ensures flexibility.
The adoption triangle from the outside angle
So far, we have talked about the cryptocurrency ecosystem mainly from the inside angle. It was a phase in which the cryptocurrencies were born so the only limited number of people got in touch with them. Let’s now focus more on the outside angle of the adoption triangle. This is much more important since technology is not useful when it is not adopted.
If decentralization or security deteriorates, someone can change digital scarcity. Alternatively, some other fraud may occur. Cryptocurrencies are not only tasked with maintaining digital scarcity but have also taken responsibility for transferring value. It is not the case for gold and it is a very complex task closely linked to the technological category. Gold is naturally global and cryptocurrencies strive for the same. If we are to talk about value transfer, it must also work on a global scale. However, the first generation of cryptocurrencies cannot do this and fall far short of people’s expectations in terms of scalability. Thus transactions might be slow and expensive.
The technological aspect of cryptocurrencies allows competition between different projects. Every technology can be improved or even replaced. There is always room for innovation and greater efficiency. At this point, the technological aspect is not in line with the economic aspect. From an economic point of view, people expect some kind of stability and best-quality properties. At least if we are talking about sound money. Gold was chosen as an underlying asset for sound money due to its first-class properties that no other asset can challenge. If we were to compare individual projects only according to technological quality, we would never achieve the required stability. Imagine a project that has slow and expensive transactions. What if there is another new project that will resolve the problem and will have fast and cheap transactions. Which project will people use more likely? Will people choose by technology or current adoption? Hard to predict the future.
 Who is going to win?
Who is going to win?
Natural resources such as gold, silver, or iron have stable properties and different scarcity. These properties are given by nature. It won’t change. As we pointed out above, creating a digital scarcity is easy. However, in order to maintain it in the long run, we must carefully examine the individual properties of the projects. What properties? We haven’t actually agreed on that yet. The majority of people have not reached a consensus. The adoption triangle defines three categories. Therefore, in addition to technology, we must also examine the economic and social aspects.
The social aspect directly depends on the technological aspect. The adoption of cryptocurrencies depends only on whether people will be able to use them globally. The emerging third generation of cryptocurrencies is likely to defeat the first generation from in technological category. The first generation, led by Bitcoin, is currently the most adopted. Nevertheless, adoption is very low and less than one percent of the population owns cryptocurrencies right now.
In order to talk about sound money, we need to achieve mass adoption. The reason is quite simple. The majority of the population must agree on sound money that will be based on digital scarcity. Sound money will not work if only a minority agrees. And let us not forget the role of states and central banks. These institutions still have a strong say and a fundamental influence on the citizens of their countries. No sound money can be created and adopted without their consent or acceptance of digital scarcity as a standard. That is unless we anticipate a revolution that would disrupt existing state structures.
Fiat money is used because of a government’s order and must be accepted as a means of payment. People just accept the fact and follow the rules. In the case there will be some troubles with fiat money, governments have many other options than to accept a particular cryptocurrency as sound money. That’s just a fact. Moreover, opinions on that topic might differ from state to state. If a state A accepts some project as sound money and owns 60% of coins than state B will probably not do the same. Just because it would be disadvantageous and there are so many alternatives. State B would rather create own project or accept another one. The basic economic rules apply equally to retail, banks, and states. Everybody with skin in the game will push a particular project. This is natural and selfish behavior. It is much easier for states to make their own digital currency than to accept a global one. In this way, states will retain their dominant position. Does it even make sense to get rid of states and let a new group of rich people emerge? We don’t know. Remember, the concept of digital scarcity can be easily copied. Sound money that would be based on digital scarcity is not only about technology but rather about the social category. The development of adoption will go in more directions. Some projects will be adopted by people. Other projects will be used by businesses, banks, and states.






